Introduction
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) is a regional group formed to promote economic integration, development, and cooperation among West African nations. For Nigerian businesses—especially those involved in logistics, import/export, and regional trade—understanding ECOWAS is essential to navigating cross-border commerce efficiently and legally.
1. What Is ECOWAS?
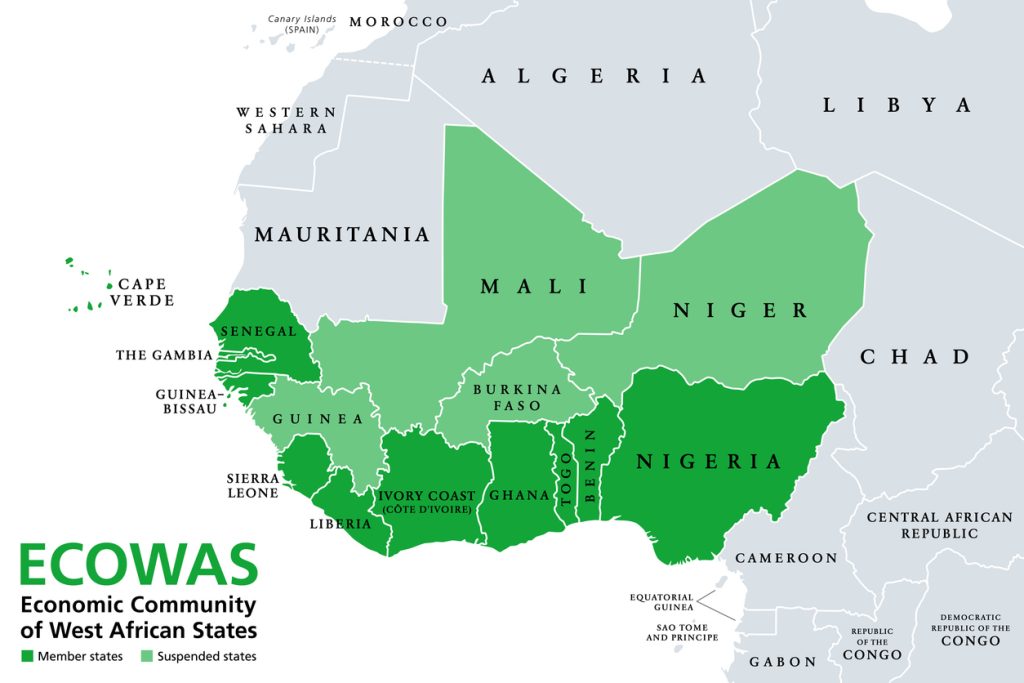
ECOWAS, short for the Economic Community of West African States, is a political and economic union of 15 countries in West Africa. Established on May 28, 1975, through the Treaty of Lagos, its primary goal is to foster collective self-sufficiency by creating a unified economic and trading space.
2. Member Countries
ECOWAS is made up of the following 15 countries:
- Nigeria
- Ghana
- Senegal
- Ivory Coast
- Benin
- Togo
- Burkina Faso
- Guinea
- Mali
- Niger
- Sierra Leone
- Liberia
- Gambia
- Guinea-Bissau
- Cape Verde
Nigeria is the largest member in terms of population and economic size, playing a central role in ECOWAS policymaking and enforcement.
3. Goals and Objectives of ECOWAS
- Economic integration across West Africa
- Free movement of people, goods, and capital
- Harmonized customs procedures and trade policies
- Establishment of a common external tariff (CET)
- Conflict resolution and political stability in the region
- Development of infrastructure for transport, energy, and ICT
4. Key Trade Mechanisms Under ECOWAS
A. ECOWAS Trade Liberalization Scheme (ETLS)
ETLS is the main operational tool for promoting free trade within the region. It allows approved products from ECOWAS countries to be traded duty-free.
B. ECOWAS Common External Tariff (CET)
This unifies import duties across the region and simplifies customs procedures.
C. ECOWAS Brown Card
A motor vehicle insurance scheme that provides cross-border coverage in member states—useful for freight and haulage operators.
D. ECOTIS (ECOWAS Trade Information System)
An online portal offering trade intelligence, tariffs, and regulatory procedures for businesses.
5. Benefits for Nigerian Businesses
- Duty-free access to regional markets via ETLS
- Streamlined customs processes through CET and regional digital platforms
- Increased logistics efficiency for haulage and freight movement
- Access to regional insurance and driver licenses recognized across borders
- Support for SMEs and exporters expanding into neighboring countries
6. Challenges and Ongoing Reforms
Despite its progress, ECOWAS faces some challenges:
- Non-tariff barriers like road checkpoints and unofficial fees
- Inconsistent policy implementation across member states
- Infrastructural deficits, especially in border areas
- Political instability in parts of the region
Reform programs—such as ECOWAS’s digital customs systems, transport corridors, and AfCFTA alignment—aim to overcome these issues.
Conclusion
ECOWAS plays a critical role in shaping the future of commerce, logistics, and regional cooperation in West Africa. For Nigerian businesses, it offers unmatched opportunities to trade, transport, and grow beyond borders. By leveraging ECOWAS’s tools like the ETLS, CET, and ECOTIS, companies can reduce costs, access new markets, and operate more efficiently within West Africa’s integrated economy.
Need support moving goods across ECOWAS borders? Contact Travo.ng for expert guidance on customs clearance, bonded terminals, driver hire, and regional logistics.